Mini-Grids
Africa Minigrids Program (AMP): Powering Rural Africa with Sustainable Energy Solutions

The Africa Minigrids Program (AMP) stands as a country-led technical assistance initiative aimed at minigrid development across 21 initial African countries. The program's explicit focus is on nurturing early-stage minigrid markets, with a primary objective of establishing a conducive environment to attract substantial private investments. Supported by GEF funding, the United Nations Development Programme, in partnership with the Rocky Mountain Institute (RMI) and the African Development Bank (AfDB), spearheads the program, engaging a broad spectrum of minigrid stakeholders in Africa and beyond.
This comprehensive initiative represents a collaborative effort involving multiple partners. With GEF funding, the United Nations Development Programme collaborates with the Rocky Mountain Institute (RMI) and the African Development Bank (AfDB), linking up with a diverse range of minigrid stakeholders across Africa. Amid various ongoing initiatives, the AMP supplements and complements the existing efforts to foster minigrid markets across the continent, fostering increased collaboration and partnerships during its implementation.
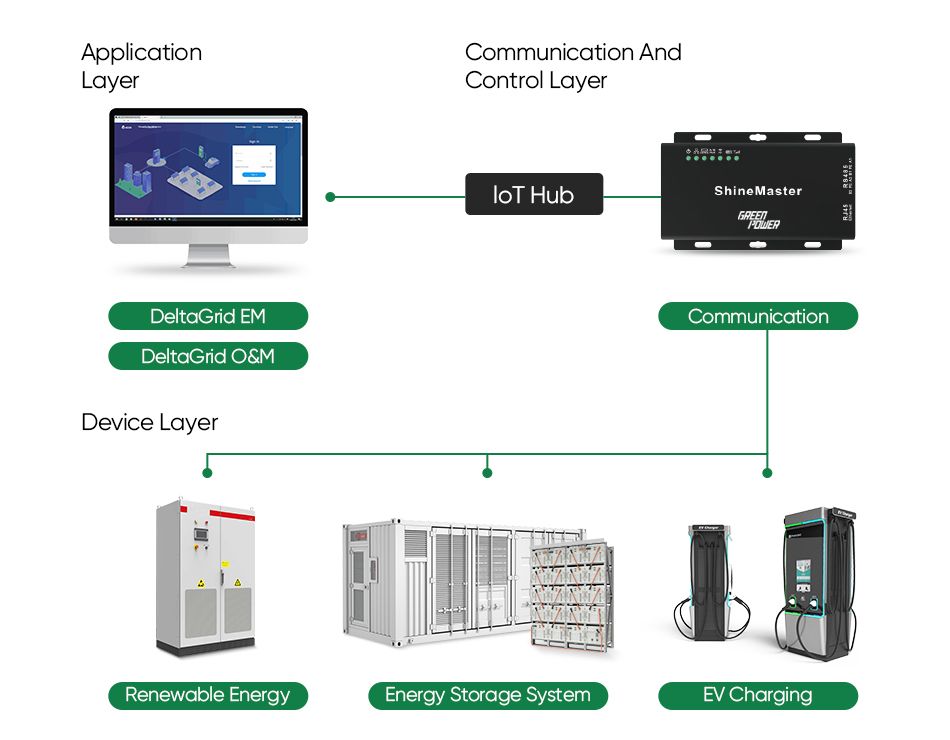
Understanding Minigrids
A minigrid, also known as a "microgrid" or "isolated grid," refers to an interconnected system of electricity generators and potential energy storage systems tied to a distribution network catering to a localized cluster of consumers. These grids involve small-scale electricity generation (ranging from 10 kW to 10 MW) that serves a limited number of users via a distribution grid capable of operating independently of national electricity transmission networks.Contact us to customize a proper Minigrid
Unlike single customer systems, such as solar home systems (SHS), minigrids possess the unique capability to function autonomously, disconnected from a centralized grid. However, they can be designed to connect with the central grid, primarily operating within it, maintaining connection unless necessitated by power quality concerns, such as in the event of central grid failure.
Significance of Minigrids
Renewable energy minigrids, particularly solar-battery minigrids, hold immense potential in addressing the 733 million people globally—567 million of whom reside in sub-Saharan Africa—currently lacking access to electricity. This opportunity stems from decreasing hardware costs, including solar modules, batteries, and energy-efficient appliances, coupled with disruptive digital trends and innovative private sector business models.
AMP's Geographic Coverage
The AMP's primary form of country participation involves National Projects. The initial round comprises 11 countries approved in the GEF's December 2019 work program. These countries include Angola, Burkina Faso, Comoros, Djibouti, Ethiopia, Eswatini, Madagascar, Malawi, Nigeria, Somalia, and Sudan. Further rounds have been scheduled for additional countries, with projects expected to commence in 2023, following a 12-month delay after the first round.
AMP's coverage encompasses 21 countries, collectively representing 396 million people without access to electricity, comprising more than two-thirds of Africa's unelectrified population. These nations span diverse market sizes, linguistic backgrounds, geographical conditions, and post-crisis scenarios, contributing to a rich blend of contexts, perspectives, and experiences within the program.
GreenPower's Role in AMP
GreenPower, a professional energy storage manufacturer and a leading integrated provider of photovoltaic solar energy storage solutions, is dedicated to supplying more reliable and efficient solar energy solutions in rural African areas. Our successful implementation of multiple microgrid projects in Nigeria, Rwanda, Senegal, Madagascar, and other regions underscores our expertise in enhancing power supply through microgrid solutions. We aim to extend our support and expertise to improve power supply across more regions in Africa. Reach out to us to discover more.